Passive Home Design Plans
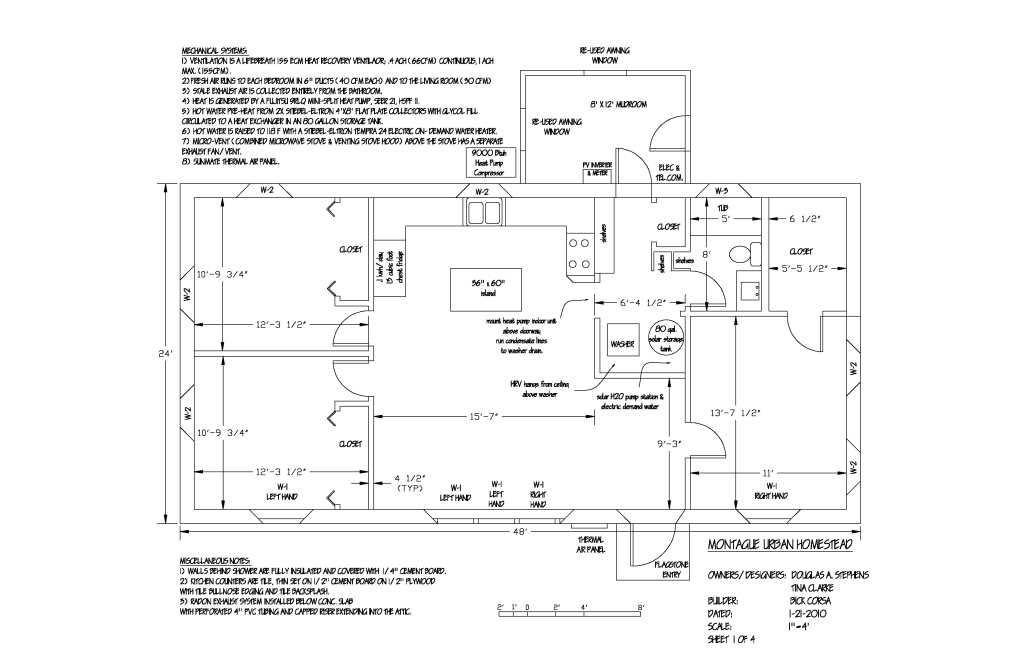
Passive Home Design Plans: A Comprehensive Guide
Definition
Passive home design is an architectural approach that prioritizes energy efficiency and thermal comfort by harnessing natural resources such as sunlight, natural ventilation, and thermal mass. These homes are designed to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature year-round without the need for conventional heating or cooling systems.
Types
There are various types of passive home designs, each tailored to specific climatic conditions and building orientations. Some common types include:
Direct Gain Passive Homes:
These homes feature large south-facing windows that allow sunlight to enter and heat the interior during the day. Thermal mass, such as concrete floors or brick walls, absorbs and stores the heat, releasing it gradually at night.
Indirect Gain Passive Homes:
These homes use a sunroom or greenhouse to collect solar heat, which is then transferred to the main living space through thermal mass or air circulation.
Hybrid Passive Homes:
These homes combine passive design principles with active systems, such as heat pumps or solar panels, to enhance energy efficiency further.
Differences
Passive home designs differ from conventional homes in several key aspects:
Energy Efficiency:
Passive homes are highly energy-efficient, reducing energy consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional homes.
Thermal Comfort:
Passive homes maintain a comfortable indoor temperature year-round without the need for conventional heating or cooling systems.
Sustainability:
Passive homes promote sustainability by reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Ease
Designing and building a passive home requires careful planning and attention to detail. However, with proper knowledge and expertise, it is possible to create a passive home that is both energy-efficient and comfortable.
Process
The process of designing and building a passive home typically involves:
Site Analysis:
Assessing the site’s orientation, solar access, and wind patterns to determine the optimal design.
Energy Modeling:
Using computer simulations to predict the home’s energy performance and identify areas for improvement.
Material Selection:
Choosing materials with high thermal performance, such as insulated windows, airtight construction, and thermal mass.
Construction:
Implementing passive design principles during construction, including proper insulation, air sealing, and solar orientation.
Advantages
Passive home design offers numerous advantages:
Energy Savings:
Passive homes significantly reduce energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills and long-term savings.
Improved Comfort:
Passive homes maintain a consistent indoor temperature, eliminating drafts and hot or cold spots.
Health Benefits:
Passive homes promote better indoor air quality by reducing moisture and pollutants.
Environmental Sustainability:
Passive homes reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable built environment.
Increased Property Value:
Passive homes are increasingly sought after by environmentally conscious buyers, resulting in potential property value appreciation.
Disadvantages
While passive home design offers many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks:
Higher Initial Cost:
Building a passive home can involve higher upfront costs due to the use of specialized materials and construction techniques.
Site Limitations:
Passive home design is most effective in areas with ample sunlight and favorable wind patterns.
Design Constraints:
Passive home design may limit certain architectural features, such as large windows on the north side of the home.
Maintenance:
Passive homes require regular maintenance, including air sealing and window cleaning, to ensure optimal performance.
Professional Expertise:
Designing and building a passive home requires specialized knowledge and expertise, which may not be readily available in all areas.
How to Design a Passive Home
Designing a passive home involves considering several key factors:
Orientation:
Position the home to maximize solar exposure and natural ventilation.
Insulation:
Use high-performance insulation materials to minimize heat loss and gain.
Air Sealing:
Seal all gaps and cracks in the building envelope to prevent air leakage.
Windows:
Install energy-efficient windows with low U-values and high solar heat gain coefficients.
Thermal Mass:
Incorporate materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete or brick, to store and release heat.
What to Look for in a Passive Home Design Plan
When selecting a passive home design plan, consider the following:
Climate Zone:
Ensure the plan is tailored to the specific climate zone of your location.
Energy Efficiency:
Review the estimated energy performance of the home, including heating and cooling loads.
Thermal Comfort:
Look for plans that incorporate passive design principles to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
Sustainability:
Choose plans that prioritize sustainable materials and construction practices.
Architectural Style:
Select a plan that aligns with your desired architectural style while incorporating passive design features.
Conclusion
Passive home design is an innovative approach that offers significant energy savings, improved comfort, and environmental sustainability. By harnessing natural resources and implementing passive design principles, passive homes create a more comfortable and energy-efficient living environment. While designing and building a passive home requires careful planning and specialized expertise, the long-term benefits make it a worthwhile investment for homeowners seeking a sustainable and energy-conscious lifestyle.
FAQs
Are passive homes suitable for all climates?
Passive homes can be designed for a wide range of climates, but they are most effective in areas with ample sunlight and favorable wind patterns.
Can passive homes be retrofitted to existing buildings?
Retrofitting existing buildings to passive homes is possible but can be challenging and expensive. It is generally more cost-effective to incorporate passive design principles into new construction projects.
Are passive homes expensive to maintain?
Passive homes typically require less maintenance than conventional homes due to their airtight construction and efficient systems. However, regular maintenance, such as air sealing and window cleaning, is essential to ensure optimal performance.
Closing Statement
Passive home design is a promising solution for creating energy-efficient, comfortable, and sustainable homes. By embracing passive design principles, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, improve our living environments, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for general knowledge purposes only and should not be construed as professional advice. It is recommended to consult with qualified professionals for specific guidance and recommendations related to passive home design and construction.