Passive Solar Home Design
Passive Solar Home Design: Harnessing Nature’s Energy for Sustainable Living
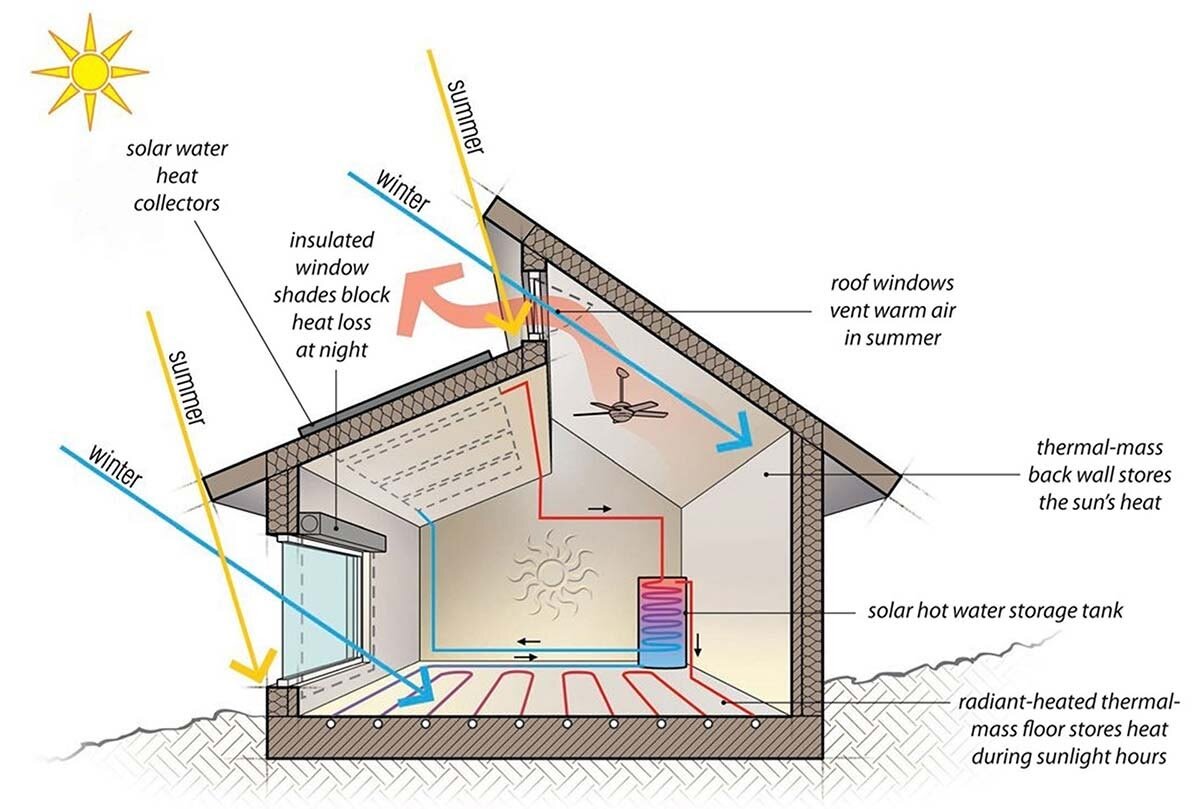
Passive solar home design is an architectural approach that utilizes natural energy sources, primarily sunlight, to heat and cool a building without relying on conventional energy systems. By incorporating passive solar design principles, homeowners can significantly reduce their energy consumption, minimize their environmental impact, and create comfortable and healthy living spaces.
Definition and Types of Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design involves harnessing the sun’s energy through the building’s structure and materials. It differs from active solar systems, which use mechanical devices such as solar panels and pumps to generate electricity or heat. Passive solar design strategies can be categorized into three main types:
Direct Gain:
This approach allows sunlight to enter the building directly through south-facing windows. The absorbed solar energy heats the interior surfaces, which then release heat into the living space.
Indirect Gain:
Sunlight is absorbed by a thermal mass, such as a concrete slab or brick wall, which stores the heat and releases it gradually into the building.
Isolated Gain:
A sunspace or greenhouse is attached to the building, acting as a buffer zone that collects solar heat and transfers it to the living space.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design offers numerous advantages:
Reduced Energy Consumption:
By utilizing natural energy sources, passive solar homes can significantly reduce their reliance on conventional heating and cooling systems, leading to lower energy bills.
Environmental Sustainability:
Passive solar design minimizes greenhouse gas emissions by reducing the need for fossil fuels, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
Improved Indoor Comfort:
Passive solar homes provide even and comfortable temperatures throughout the year, eliminating drafts and hot spots.
Increased Property Value:
Homes with passive solar features are often more desirable to buyers, resulting in potential increases in property value.
However, there are also some drawbacks to consider:
Site Orientation:
Passive solar design requires a building to be oriented in a way that maximizes solar exposure, which may not always be possible.
Seasonal Limitations:
Passive solar design is most effective during the winter months when the sun’s angle is lower. In summer, overheating may occur if proper shading strategies are not implemented.
Initial Cost:
Incorporating passive solar design features into a building can increase the initial construction costs, although these costs can be offset over time through energy savings.
How to Implement Passive Solar Design
Implementing passive solar design involves a holistic approach that considers the following factors:
Building Orientation:
The building should be oriented to maximize exposure to the sun’s rays during the winter months.
Window Placement:
South-facing windows should be large and well-insulated to allow for maximum solar heat gain.
Thermal Mass:
Materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete or brick, should be incorporated into the building’s structure to store and release heat.
Shading:
Overheating during the summer months can be prevented by using overhangs, awnings, or deciduous trees to shade windows.
Ventilation:
Natural ventilation strategies, such as cross-ventilation and stack effect, can be used to circulate air and maintain comfortable temperatures.
Conclusion
Passive solar home design is a sustainable and cost-effective approach to creating comfortable and energy-efficient living spaces. By harnessing the sun’s energy, passive solar homes reduce reliance on fossil fuels, minimize environmental impact, and provide numerous benefits to homeowners. As the world becomes increasingly aware of the need for sustainable living, passive solar design is poised to play a significant role in the future of residential architecture.
FAQ
Is passive solar design only suitable for warm climates?
No, passive solar design can be effective in both warm and cold climates. In cold climates, passive solar design helps reduce heating costs, while in warm climates, it can help reduce cooling costs.
Can passive solar design be used in existing homes?
Yes, it is possible to retrofit existing homes with passive solar design features. However, the extent of the retrofit will depend on the specific design of the home.
How much energy can I save with passive solar design?
The amount of energy savings will vary depending on the climate, the size of the home, and the specific design features implemented. However, studies have shown that passive solar homes can reduce energy consumption by up to 50%.
Closing Statement
Passive solar home design is a valuable tool for creating sustainable and energy-efficient homes. By incorporating passive solar design principles into their homes, homeowners can reduce their energy consumption, minimize their environmental impact, and create comfortable and healthy living spaces.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and educational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice from a qualified architect or engineer.