Energy Efficient Home Design
Energy Efficient Home Design: A Comprehensive Guide
Energy-efficient home design has become increasingly important in today’s world, where rising energy costs and environmental concerns are driving the need for sustainable and cost-effective housing solutions. By incorporating energy-efficient features into the design and construction of homes, homeowners can significantly reduce their energy consumption, lower their utility bills, and contribute to a greener planet.
Definition and Types of Energy Efficient Homes
Definition: Energy-efficient homes are designed and built to minimize energy consumption while maintaining a comfortable and healthy living environment. They incorporate various features that reduce heat loss, improve insulation, and utilize renewable energy sources.
Types: There are several types of energy-efficient homes, including:
- Passive House: Designed to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature without the need for active heating or cooling systems.
- Net Zero Home: Produces as much energy as it consumes, resulting in zero net energy usage.
- LEED-Certified Home: Meets specific environmental and energy-efficiency standards set by the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) program.
Benefits and Challenges of Energy Efficient Homes
Benefits:
- Reduced Energy Costs: Energy-efficient homes consume less energy, leading to lower utility bills.
- Increased Comfort: Proper insulation and air sealing reduce drafts and temperature fluctuations, ensuring a more comfortable living environment.
- Improved Air Quality: Energy-efficient homes often incorporate ventilation systems that improve indoor air quality by removing pollutants and allergens.
- Environmental Sustainability: By reducing energy consumption, energy-efficient homes contribute to a greener planet by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Increased Resale Value: Energy-efficient homes are in high demand and can command higher resale prices.
Challenges:
- Higher Initial Costs: Energy-efficient features can add to the initial construction costs of a home.
- Design Limitations: Some energy-efficient features may require specific design considerations, which can limit architectural flexibility.
- Maintenance Requirements: Certain energy-efficient systems, such as solar panels, may require regular maintenance.
- Skilled Labor: Energy-efficient home design and construction require specialized knowledge and skills, which may not be readily available in all areas.
- Occupant Behavior: The energy efficiency of a home can be affected by occupant behavior, such as thermostat settings and lighting habits.
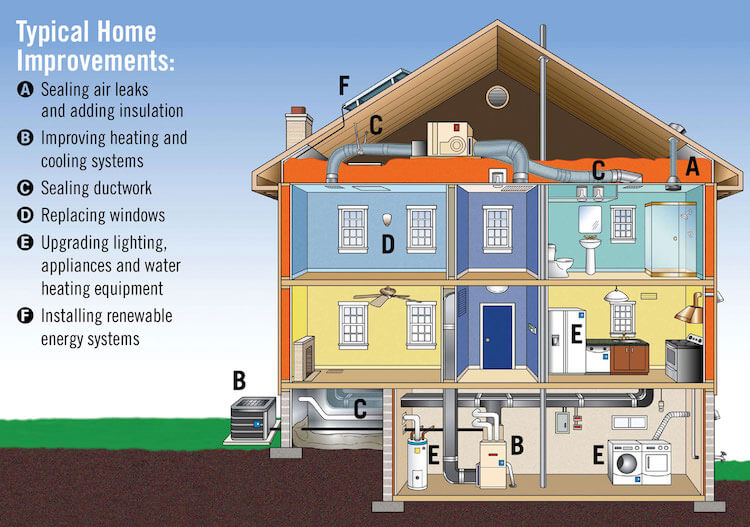
How to Design an Energy Efficient Home
Planning and Design:
- Orientation: Position the home to maximize natural sunlight and reduce heat gain.
- Insulation: Use high-quality insulation in walls, ceilings, and floors to minimize heat loss.
- Air Sealing: Seal gaps and cracks around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent air leakage.
- Windows and Doors: Choose energy-efficient windows and doors with low U-values and high R-values.
- HVAC System: Install a high-efficiency heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system that meets the specific needs of the home.
Renewable Energy:
- Solar Panels: Generate electricity from sunlight to offset energy consumption.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: Utilize the earth’s constant temperature to heat and cool the home.
- Wind Turbines: Generate electricity from wind power.
Other Features:
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Choose appliances with Energy Star ratings to reduce energy consumption.
- LED Lighting: Use LED light bulbs, which are more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Smart Home Technology: Install smart thermostats and other devices to optimize energy usage.
Conclusion
Energy-efficient home design is essential for creating sustainable and cost-effective housing solutions. By incorporating energy-saving features into the design and construction of homes, homeowners can significantly reduce their energy consumption, lower their utility bills, and contribute to a greener planet. While there may be some challenges associated with energy-efficient homes, the long-term benefits far outweigh the drawbacks.
FAQs
Q: What is the most important factor in energy-efficient home design?
A: Insulation is the most important factor in energy-efficient home design, as it prevents heat loss and reduces the need for heating and cooling.
Q: How much can I save on my energy bills with an energy-efficient home?
A: The amount you can save on your energy bills depends on several factors, including the size of your home, the climate you live in, and the specific energy-efficient features you incorporate. However, studies have shown that energy-efficient homes can reduce energy consumption by up to 50%.
Q: Is it worth it to invest in energy-efficient features?
A: Yes, it is worth it to invest in energy-efficient features. While the initial costs may be higher, the long-term savings on energy bills can offset the investment. Additionally, energy-efficient homes are in high demand and can command higher resale prices.
Closing Statement
Energy-efficient home design is a smart investment that benefits both homeowners and the environment. By embracing energy-saving features, we can create a more sustainable and cost-effective future for ourselves and generations to come.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as professional advice. Consult with a qualified architect or energy efficiency expert for specific guidance on designing an energy-efficient home.